LIBRETTO 431
Trial Design
LIBRETTO-431: A Phase III superiority trial of Retevmo versus chemotherapy with or without pembrolizumab for patients with RET fusion-positive advanced or metastatic NSCLC6-8
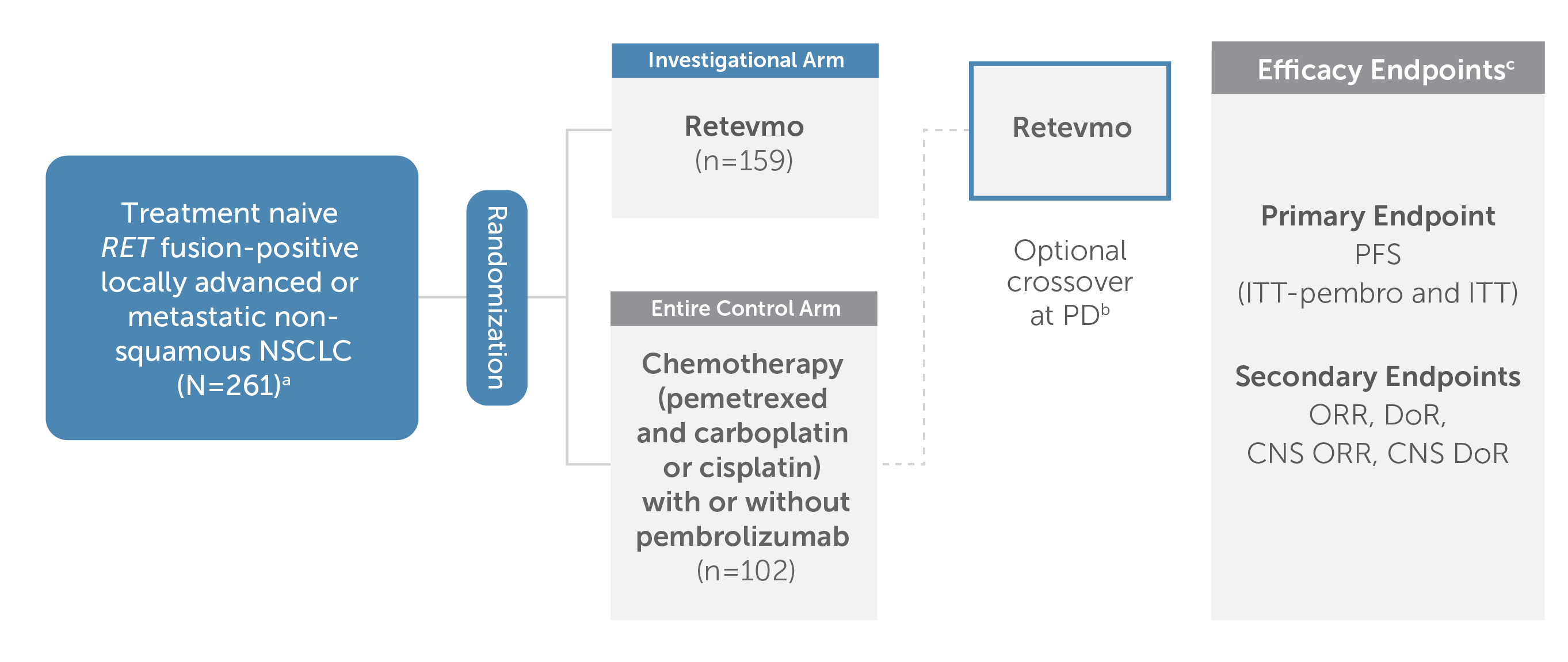
Chart showing trial design for LIBRETTO-431, a randomized, global, multicenter, open-label, Phase III trial that evaluated Retevmo versus chemotherapy (pemetrexed and carboplatin or cisplatin) with or without pembrolizumab in treatment-naive adult patients with RET fusion-positive advanced or metastatic non-squamous NSCLC. Of the 261 total patients enrolled, 159 patients were randomized to Retevmo and 102 patients were randomized to chemotherapy with or without pembrolizumab.
Crossover to Retevmo was optional for patients in the control arm upon confirmed progression as evaluated by IRC.
aPatients with brain metastases were eligible to be enrolled if asymptomatic and neurologically stable for 2 weeks.
bThe crossover rate to Retevmo on study was 61.8% (n=42/68). Off-study crossover to a selective RET inhibitor occurred in an additional 15% of patients. The primary efficacy endpoint was PFS for Retevmo, evaluated in ITT-pembro and in ITT populations; secondary endpoints included ORR, DoR, CNS ORR, and CNS DoR.
cAll primary and secondary endpoints listed were assessed by IRC per RECIST v1.1. CNS ORR and CNS DoR were also assessed per RANO-BM.
Efficacy presentation focuses on the cohort of patients that investigators intended to treat with pembrolizumab (ITT-pembro), which included 129 patients who were randomized to Retevmo and 83 patients who were randomized to pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy.
Retevmo was dosed at 160 mg BID. Pembrolizumab was dosed at 200 mg Q3W. Chemotherapy included pemetrexed (500 mg/m2 Q3W) and carboplatin (AUC 5 Q3W) or cisplatin (75 mg/m2 Q3W).
Patients were stratified per investigator's choice of treatment with or without pembrolizumab if randomized to the control arm. Choice was declared prior to randomization. The subset of patients randomized with the intent not to receive pembrolizumab was less than 20% of total randomized patients, and is analyzed only as part of the intent-to-treat population.
Additional stratification factors: geography, brain metastases at baseline per investigator assessment.
aPatients with brain metastases were eligible to be enrolled if asymptomatic and neurologically stable for 2 weeks.
bThe crossover rate to Retevmo on study was 61.8% (n=42/68). Off-study crossover to a selective RET inhibitor occurred in an additional 15% of patients.
cAll primary and secondary endpoints listed were assessed by IRC per RECIST v1.1. CNS ORR and CNS DoR were also assessed per RANO-BM.
AUC=area under the curve; BID=twice a day; CNS=central nervous system; DoR=duration of response; IRC=independent review committee; ITT=intent to treat; NSCLC=non-small cell lung cancer; ORR=overall response rate; PFS=progression-free survival; PD=progressive disease; Q3W=every three weeks; RANO-BM=Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology Brain Metastases; RECIST=Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumours; RET=rearranged during transfection; SOC=standard of care
PFS
In patients with advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive NSCLC
Retevmo demonstrated superior PFS compared to pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy7,9
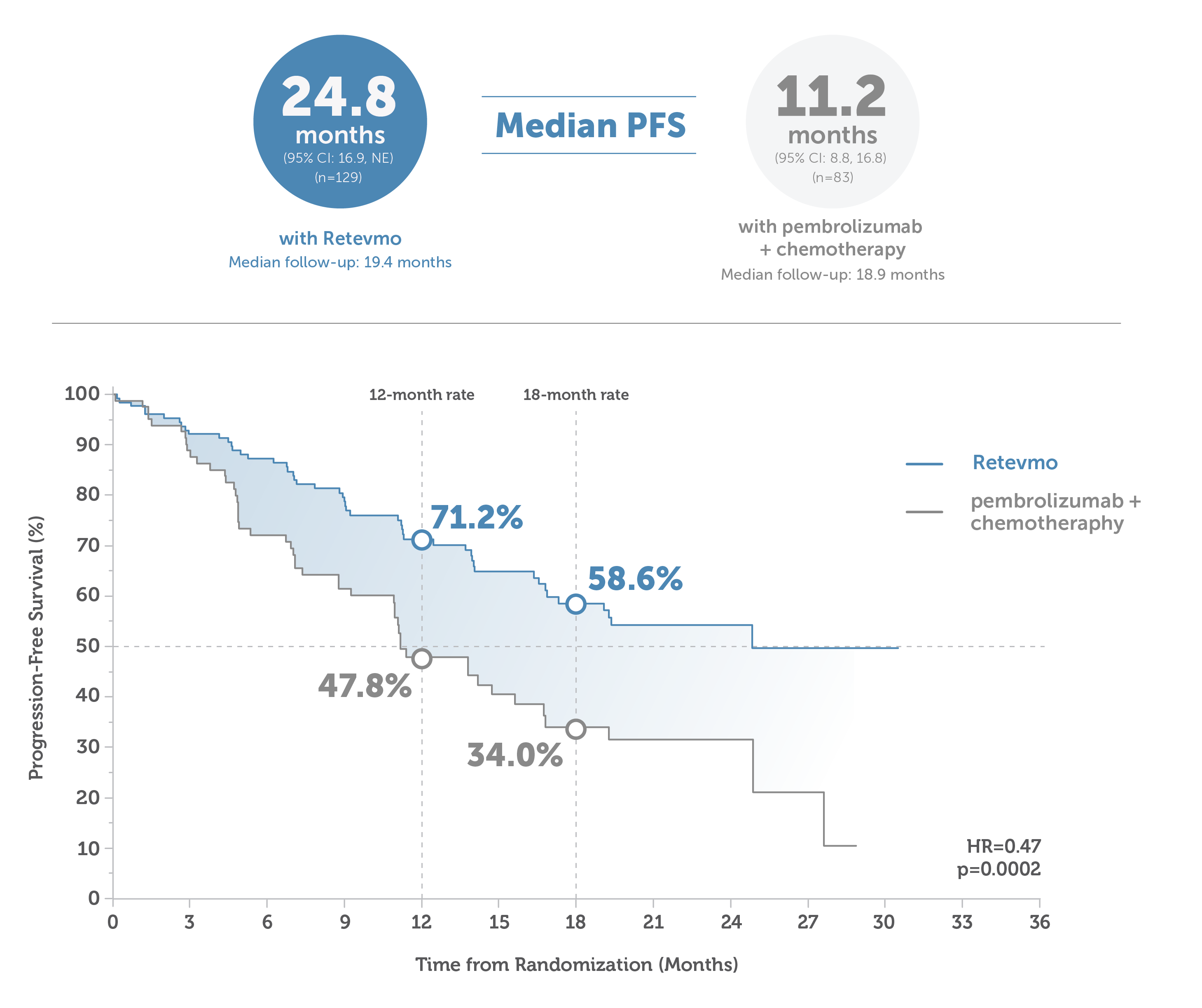
This image shows median PFS in Retevmo-treated patients versus those treated with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy. PFS was assessed in all randomized patients and was based on an interim analysis with a data cutoff date of May 1, 2023. For patients treated with Retevmo (n=129), median PFS was 24.8 months (95% CI: 16.9, NE) with median follow-up of 19.4 months. In patients treated with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy (n=83), median PFS was 11.2 months (95% CI: 8.8, 16.8), with median follow-up of 18.9 months. An accompanying Kaplan-Meier curve shows progression-free survival for Retevmo-treated patients of 71.2% at 12 months and 58.6% at 18 months. PFS for patients treated with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy was 47.8% at 12 months and 34.0% at 18 months. Hazard ratio was 0.47 (p=0.0002).
Median PFS: 24.8 months (95% CI: 17.3, NE) with Retevmo (n=159) vs 11.2 months (95% CI: 8.8, 16.8) for the entire control arm (n=102).7,9,§
PFS was assessed in all randomized patients.
Based on an interim analysis with a data cutoff date of May 1, 2023.7,9
§Median follow-up time for patients treated with Retevmo was 19.4 months. Median follow-up time for patients in the entire control arm was 16.5 months.
HR=hazard ratio; NSCLC=non-small cell lung cancer; mPFS=median progression-free survival; PFS=progression-free survival
Select Important Safety Information
Hepatotoxicity: Serious hepatic adverse reactions occurred in 3% of patients treated with Retevmo. Increased aspartate aminotransferase (AST) occurred in 59% of patients, including Grade 3 or 4 events in 11% and increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT) occurred in 55% of patients, including Grade 3 or 4 events in 12%. Monitor ALT and AST prior to initiating Retevmo, every 2 weeks during the first 3 months, then monthly thereafter and as clinically indicated. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue Retevmo based on the severity.
ORR and DoR
Objective response rate and duration of response for Retevmo vs pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy7,9
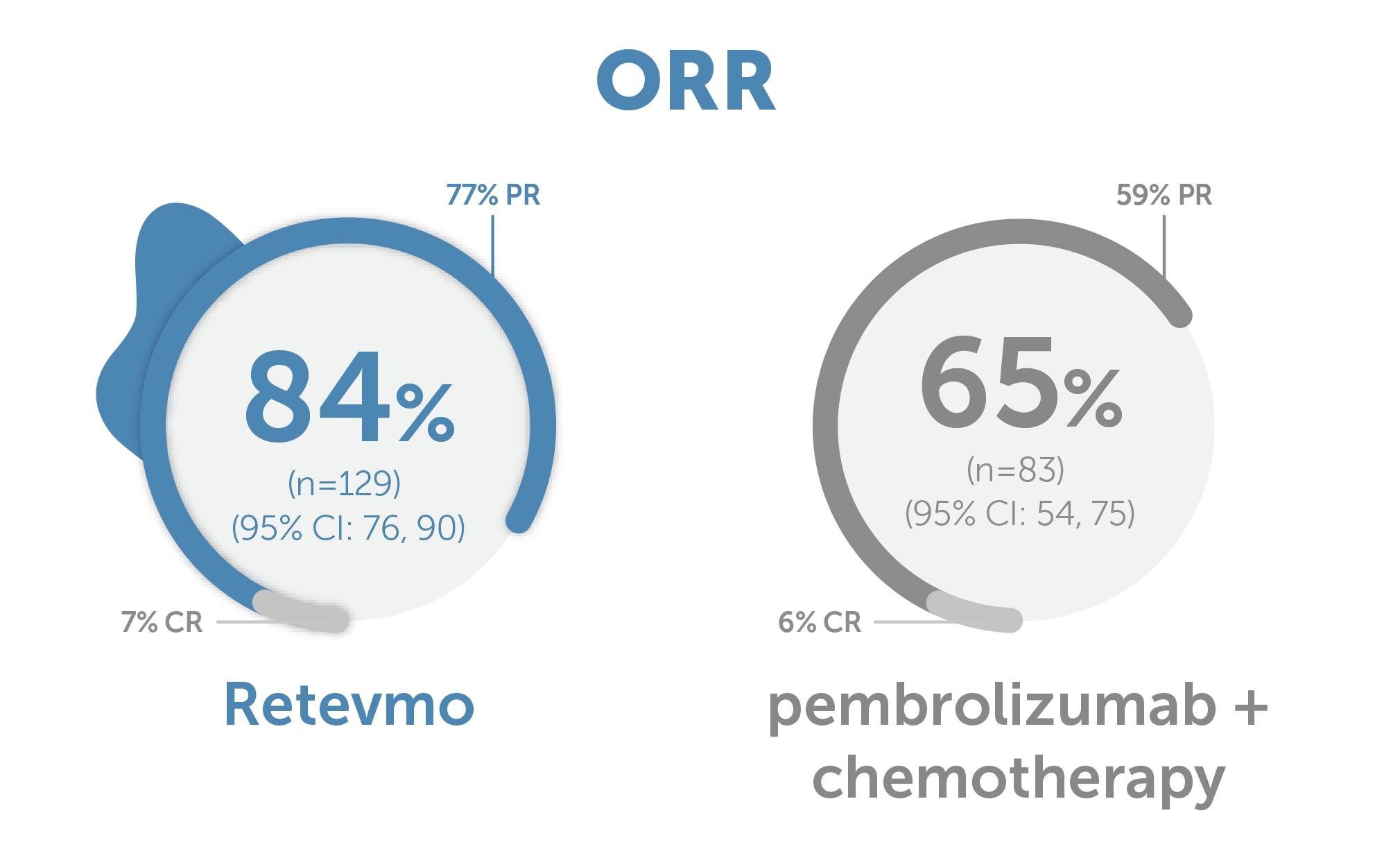
Graphic showing Objective Response Rate of 84% (95% CI: 76, 90) for Retevmo (n=129) versus 65% (95% CI: 54, 75) for pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy (n=83).7,9 Partial response (PR) for Retevmo was 77%; Complete Response (CR) for Retevmo was 7%. PR for pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy was 59%; CR for pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy was 6%.
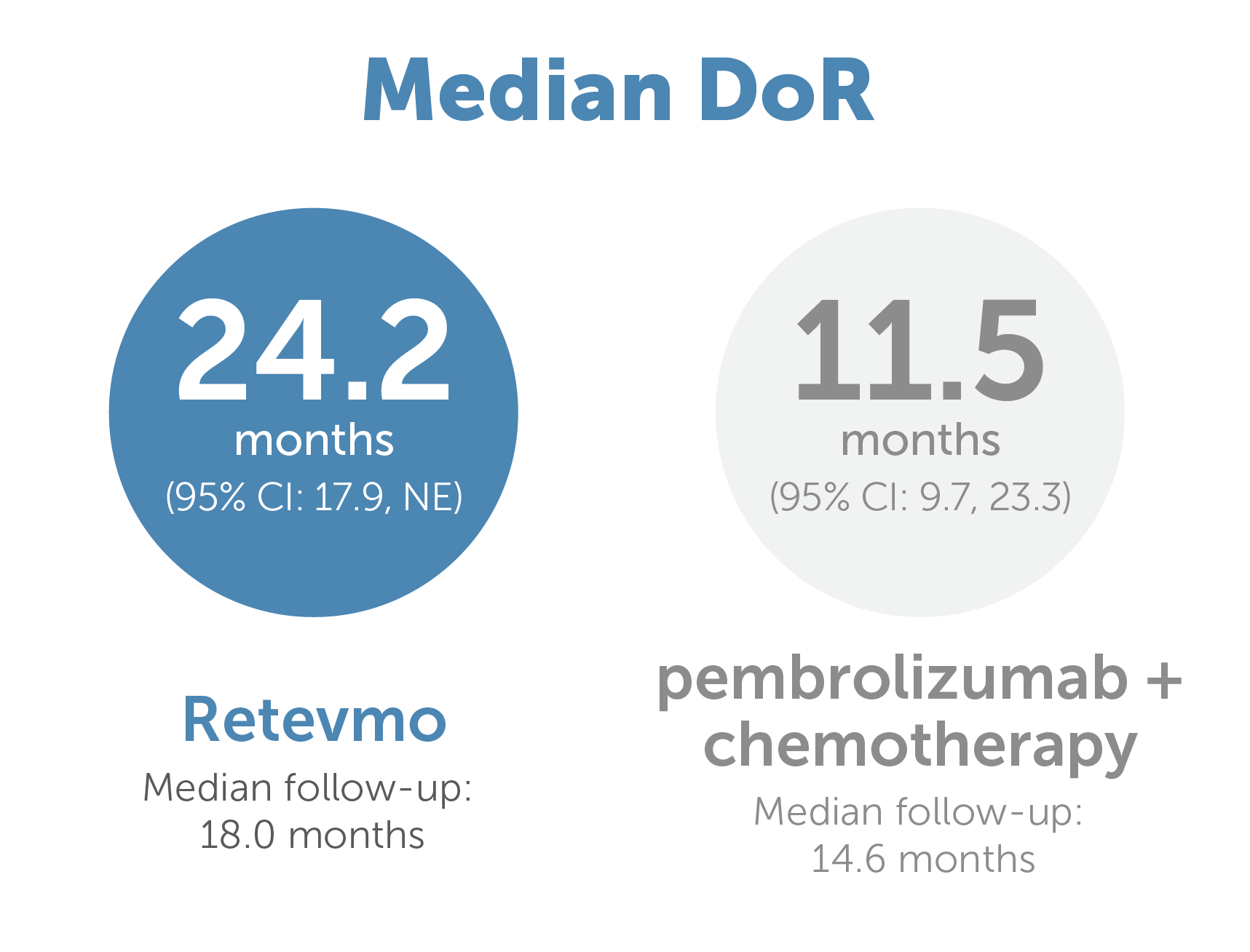
Graphic showing median Duration of Response of 24.2 months (95% CI: 17.9, NE) for Retevmo (n=129) versus 11.5 months (95% CI: 9.7, 23.3) with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy (n=83)7,9
ORR:
84% (95% CI: 77, 89; 7.5% CR + 76% PR) with Retevmo (n=159) vs 63% (95% CI: 53, 72; 4.9% CR + 58% PR) for the entire control arm (n=102)
Median DoR:
24.2 months (95% CI: 17.9, NE) Retevmo (n=159) vs 12.0 months (95% CI: 9.7, 23.3) for the entire control arm (n=102)*
ORR, a secondary endpoint, was defined as CR+PR and was assessed by the IRC according to RECIST v1.1.9 Based on an interim analysis with a data cutoff date of May 1, 2023.7,9
‖Median follow-up for patients treated with Retevmo was 18.0 months. Median follow-up time for patients in the entire control arm was 12.7 months.
CI=confidence interval; CR=complete response; DoR=duration of response; IRC=independent review committee; NE=not estimable; NSCLC=non-small cell lung cancer; ORR=objective response rate; PR=partial response; RECIST=Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumours; RET=rearranged during transfection
431 CNS ORR and DoR
Retevmo had CNS activity¶ in patients with RET fusion-positive advanced or metastatic NSCLC7,9
Responses in patients with measurable CNS metastases at baseline
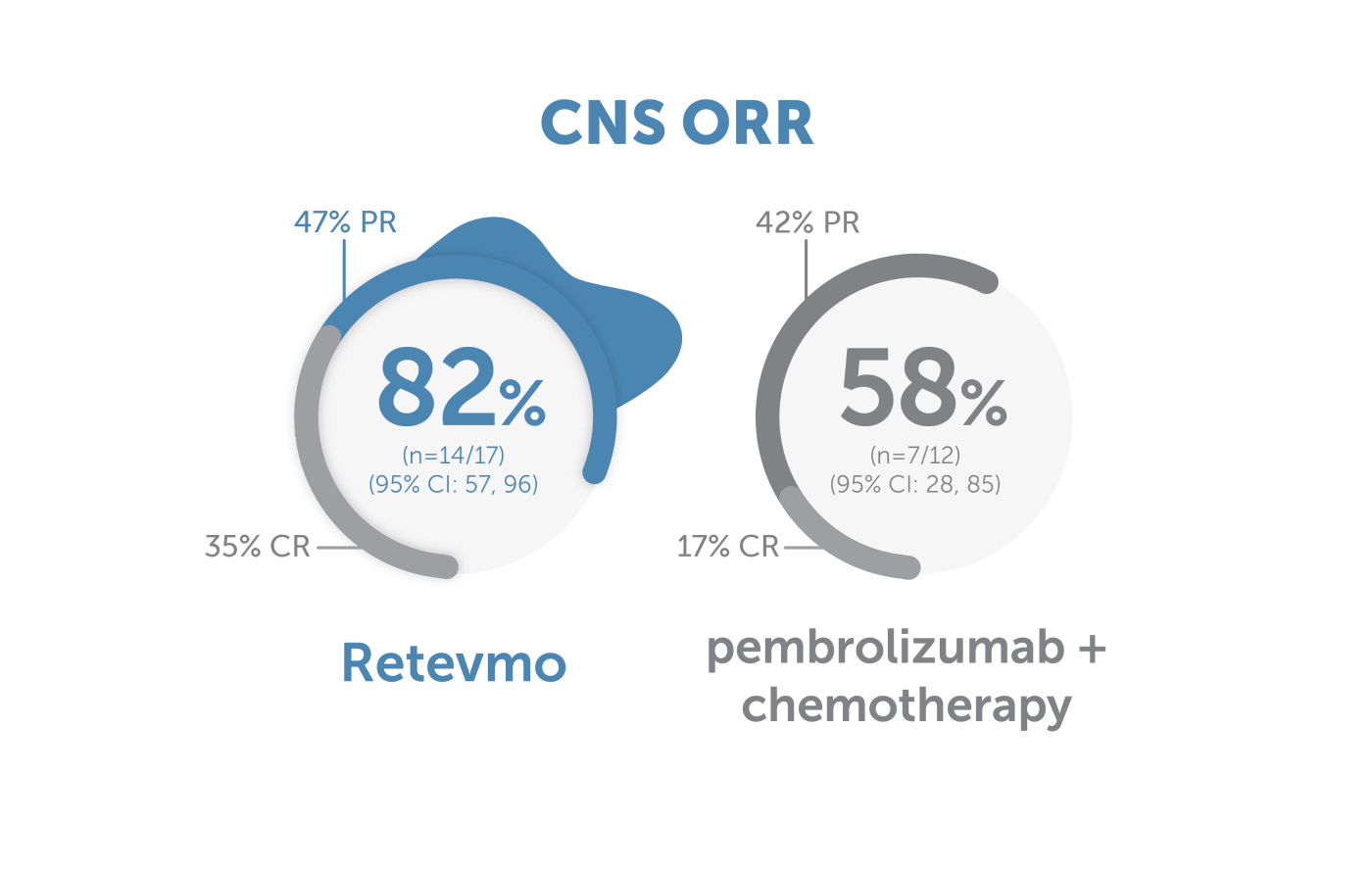
Image showing central nervous system Objective Response Rate for Retevmo versus pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy. CNS ORR for Retevmo (n=17) was 82% (95% CI: 57, 96). Within this group, 47% of patients showed partial response and 35% showed complete response. In patients treated with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy (n=12), CNS ORR was 58% (95% CI: 28, 85). Within this group, 42% of patients showed partial response and 17% showed complete response.
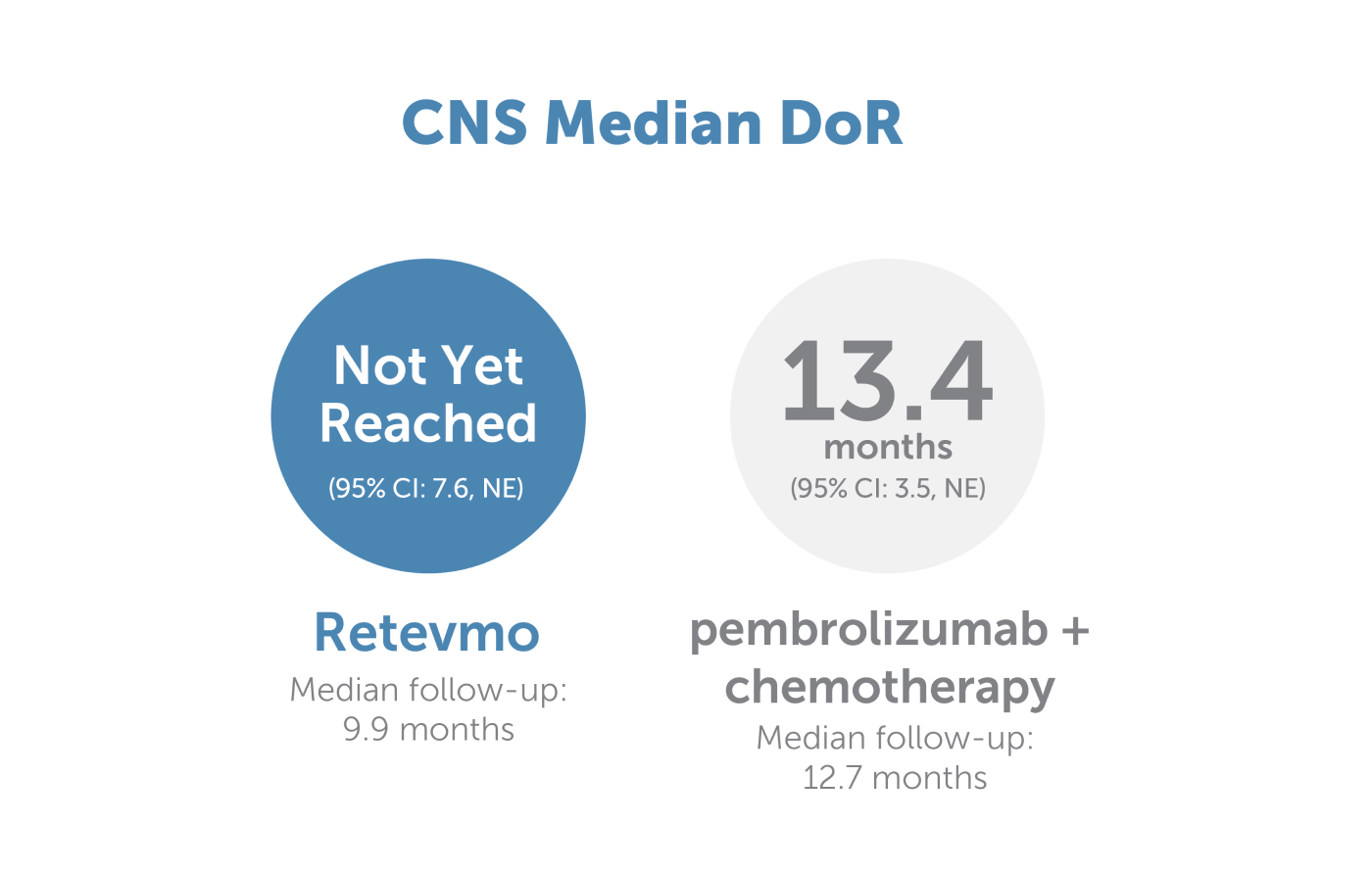
Image showing central nervous system median duration of response for Retevmo versus pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy. CNS median DoR for Retevmo (n=14) was not yet reached (95% CI: 7.6, NE). Median follow-up for this group was 9.9 months. In patients treated with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy (n=7), CNS median DoR was 13.4 months (95% CI: 3.5, NE). Median follow-up for this group was 12.7 months.
CNS Efficacy Data for Retevmo vs ITT
CNS ORR: 84% (95% CI: 60, 97; 32% CR + 53% PR) with Retevmo (n=16/19) vs 58% (95% CI: 28, 85; 17% CR + 42% PR) in the ITT (n=7/12)7,9
CNS Median DoR: NE months (95% CI: 7.4, NE) Retevmo vs 13.4 months (95% CI: 3.5, NE) in the ITT7,9,**
CNS ORR (defined as CR+PR) and CNS DoR were prespecified secondary endpoints in the LIBRETTO-431 trial and were evaluated and assessed by IRC according to RECIST v1.1.7,9
Based on an interim analysis with a data cutoff date of May 1, 2023.7,9
CI=confidence interval; CNS=central nervous system; CR=complete response; DoR=duration of response; IRC=independent review committee; ITT=intent to treat; NE=not estimable; NSCLC=non-small cell lung cancer; ORR=objective response rate; PR=partial response; RECIST=Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumours; RET=rearranged during transfection
Due to rounding, percentages presented may not add up to the indicated totals.
¶CNS activity is defined as shrinking current lesions and preventing the occurrence of new CNS lesions.
**Median follow-up for patients with measurable CNS metastases at baseline treated with Retevmo was 11.1 months. Median follow-up for patients with measurable CNS metastases at baseline in the entire control arm was 12.7 months.7,9
Select Important Safety Information
Severe, life-threatening, and fatal interstitial lung disease (ILD)/pneumonitis can occur in patients treated with Retevmo. ILD/pneumonitis occurred in 1.8% of patients who received Retevmo, including 0.3% with Grade 3 or 4 events, and 0.3% with fatal reactions. Monitor for pulmonary symptoms indicative of ILD/pneumonitis. Withhold Retevmo and promptly investigate for ILD in any patient who presents with acute or worsening of respiratory symptoms which may be indicative of ILD (e.g., dyspnea, cough, and fever). Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue Retevmo based on severity of confirmed ILD.
431 Risk of CNS Progression
Risk of CNS as the first site of progression was reduced with Retevmo compared to pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy7,9
12-Month CIR for Patients with or without Baseline CNS Metastases (N=192)7,9
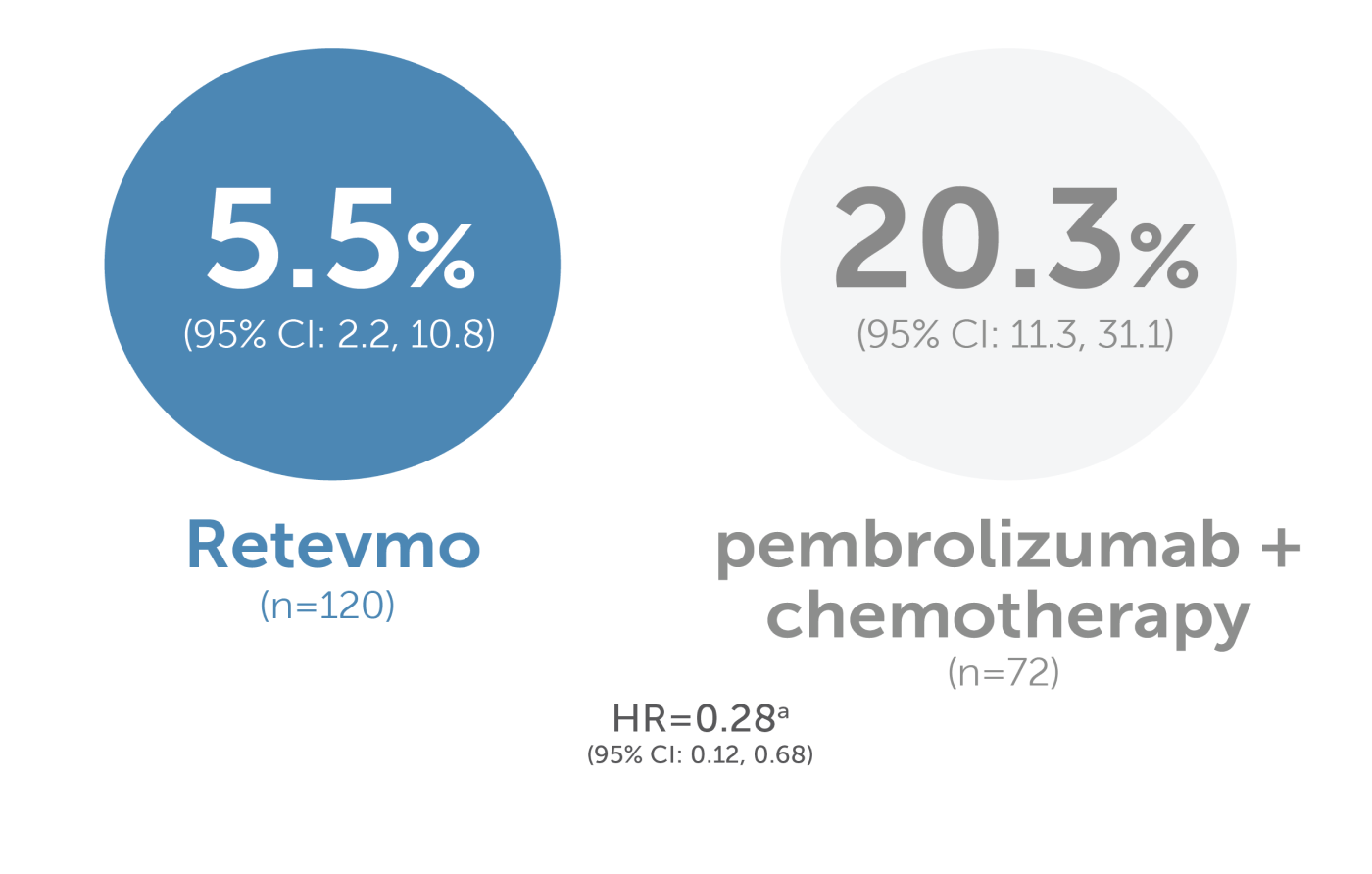
a Cause-specific HR for CNS progression accounts for competing risks of non-CNS PD and death.
The 12-month CIR for patients with and without baseline CNS metastases was 5.5% with Retevmo compared to 20.3% with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy. The 95% confidence intervals were 2.2% to 10.8% and 11.3% to 31.1%, respectively. The cause-specific hazard ratio was 0.28 with a 95% confidence interval of 0.12 to 0.68. Cause-specific HR for CNS progression accounts for competing risks of non-CNS PD and death.
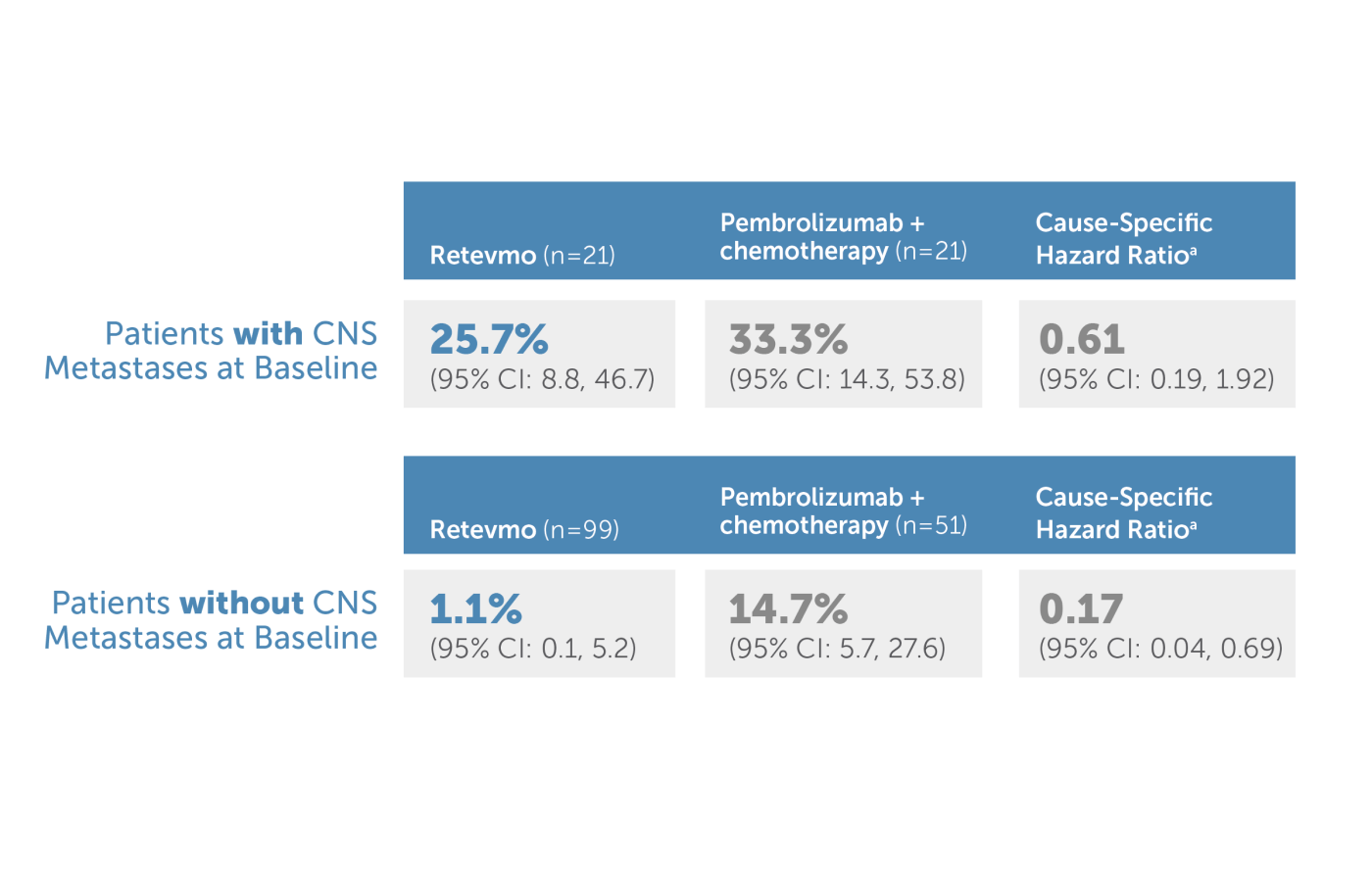
a Cause-specific HR for CNS progression accounts for competing risks of non-CNS PD and death.
The 12-month CIR for patients with baseline CNS metastases was 25.7% with Retevmo compared to 33.3% with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy. The 95% confidence intervals were 8.8% to 46.7% and 14.3% to 53.8%, respectively. The cause-specific hazard ratio was 0.61 with a 95% confidence interval of 0.19 to 1.92. The 12-month CIR for patients without baseline CNS metastases was 1.1% with Retevmo compared to 14.7% with pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy. The 95% confidence intervals were 0.1% to 5.2% and 5.7% to 27.6%, respectively. The cause-specific hazard ratio was 0.17 with a 95% confidence interval of 0.04 to 0.69. Cause-specific HR for CNS progression accounts for competing risks of non-CNS PD and death.
12-Month CIR (cumulative incidence rate) for Retevmo vs ITT7,9
With or without Baseline CNS Metastases: 5.2% (95% CI: 2.3, 9.9) with Retevmo (n=146) vs 19.4% (95% CI: 11.4, 29.1) in the ITT (n=88) [HR=0.26; 95% CI: 0.11, 0.59]
With Baseline CNS Metastases: 25.5% (95% CI: 10.0, 44.4) with Retevmo (n=25) vs 35.7% (95% CI: 17.4, 54.5) in the ITT (n=26) [HR=0.52; 95% CI: 0.19, 1.47]
Without Baseline CNS Metastases: 0.9% (95% CI: 0.1, 4.3) with Retevmo (n=121) vs 12.2% (95% CI: 4.8, 23.4) in the ITT (n=62) [HR=0.16; 95% CI: 0.04, 0.66]
Intracranial evaluation with CT or MRI was required for all patients at baseline and subsequently at the same frequency as other radiologic imaging and as clinically indicated. All results reviewed by IRC.7,9
CI=confidence interval; CIR=cumulative incidence rate; CNS=central nervous system; CT=computerized tomography; HR=hazard ratio; IRC=independent review committee; ITT=intent to treat; MRI=magnetic resonance imaging; NE=not estimable; PD=progressive disease
Safety
Safety and tolerability were evaluated in LIBRETTO-4317,10
Select Adverse Events (≥20%) in Patients Who Received Retevmo in LIBRETTO-4317,10
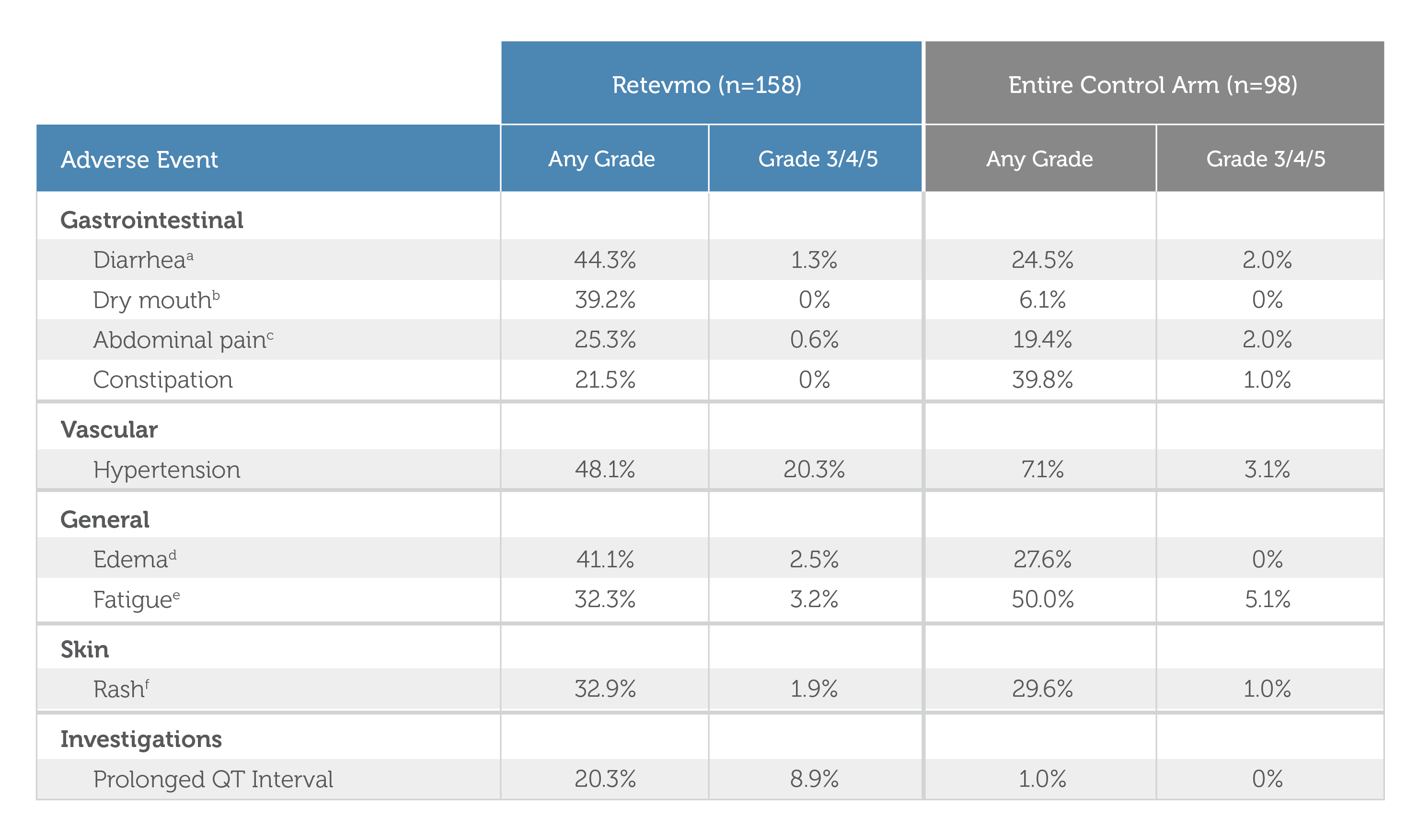
| Retevmo (n=158) | Control Arm (n=98) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Event | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4/5 | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4/5 |
| Adverse Event | ||||
| Gastrointestinal Diarrheaa | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 44.3% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4/5 1.3% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 24.5% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4/5 2.0% |
| Gastrointestinal Dry Mouthb | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 39.2% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4/5 0% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 6.1% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4/5 0% |
| Gastrointestinal Abdominal Painc | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 25.3% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4/5 0.6% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 19.4% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4/5 2.0% |
| Gastrointestinal Constipation | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 21.5% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4/5 0% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 39.8% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4/5 1.0% |
| Adverse Event | ||||
| Vascular Hypertension | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 48.1% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4/5 20.3% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 7.1% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4/5 3.1% |
| Adverse Event | ||||
| General Edemad | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 41.1% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4/5 2.5% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 27.6% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4/5 0% |
| General Fatiguee | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 32.3% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4/5 3.2% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 50.0% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4/5 5.1% |
| Adverse Event | ||||
| Skin Rashf | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 32.9% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4/5 1.9% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 29.6% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4/5 1.0% |
| Adverse Event | ||||
| Investigations Prolonged QT Interval | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 20.3% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4/5 8.9% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 1.0% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4/5 0% |
aDiarrhea includes diarrhea, anal incontinence
bDry mouth includes dry mouth, mucosal dryness
cAbdominal pain includes abdominal pain upper, abdominal pain, abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain lower, gastrointestinal pain
dEdema includes peripheral edema, face edema, edema, periorbital edema, swelling face, peripheral swelling, penile edema, scrotal edema, eye edema, eyelid edema, localized edema, orbital edema, orbital swelling, periorbital swelling
eFatigue includes fatigue, asthenia, malaise
fRash includes rash, dermatitis, rash maculo-papular, skin exfoliation, dermatitis allergic, rash macular, rash papular, rash pustular, rash erythematous, rash vesicular, urticaria
Select Laboratory Abnormalities (≥20%) Worsening from Baseline in Patients Who Received Retevmo in LIBRETTO-4317,10,a
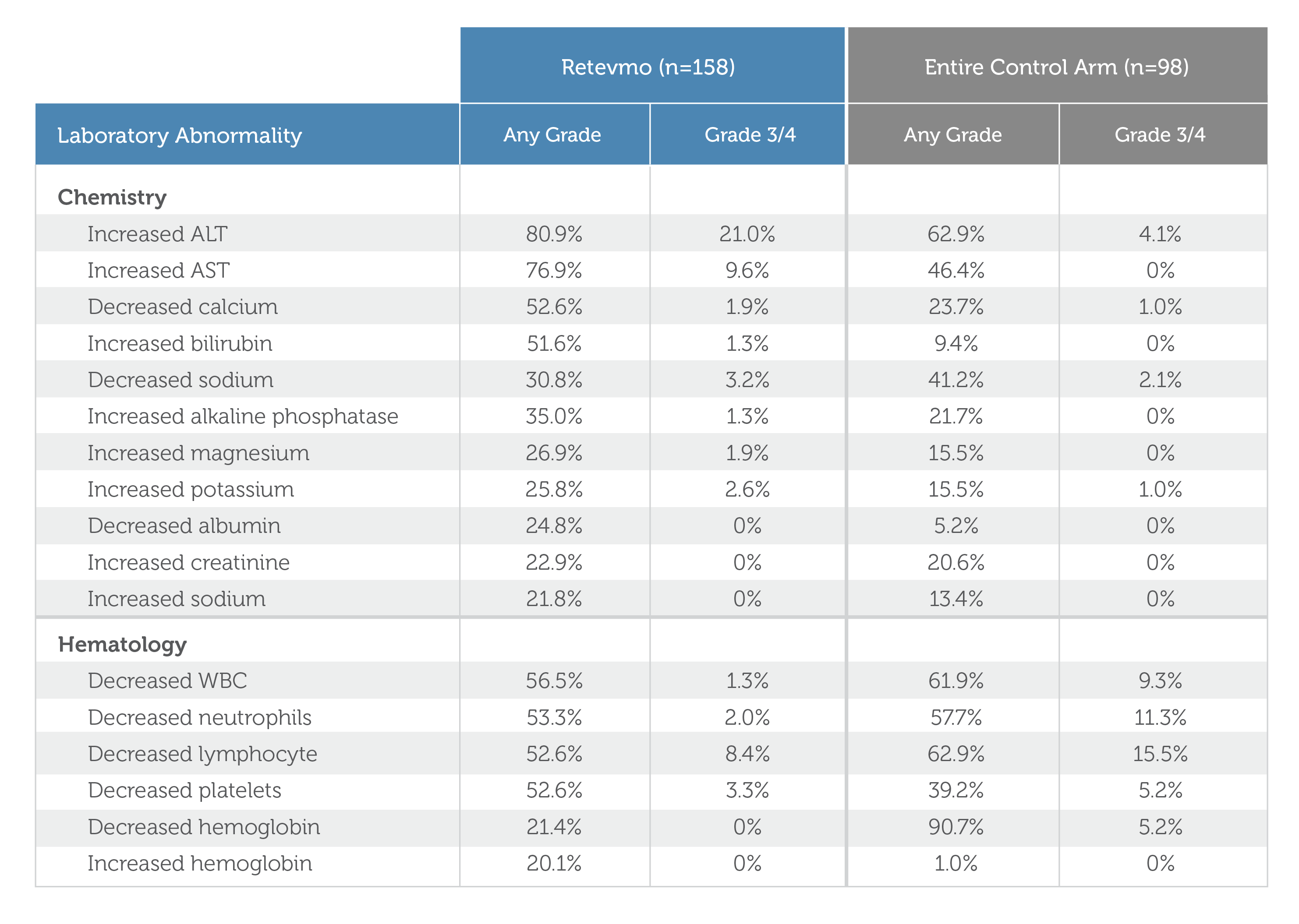
a Denominator for each laboratory parameter is based on the number of patients with a baseline and post-treatment laboratory value available, which ranged from 157 to 154 patients for Retevmo and 97 to 96 patients for the control arm.
| Retevmo (n=158) | Control Arm (n=98) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laboratory Abnormality | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4 | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4 |
| Laboratory Abnormality | ||||
| Chemistry Increased ALT | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 80.9% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4 21.0% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 62.9% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4 4.1% |
| Chemistry Increased AST | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 76.9% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4 9.6% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 46.4% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4 0% |
| Chemistry Decreased calcium | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 52.6% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4 1.9% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 23.7% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4 1.0% |
| Chemistry Increased bilirubin | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 51.6% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4 1.3% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 9.4% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4 0% |
| Chemistry Decreased sodium | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 30.8% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4 3.2% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 41.2% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4 2.1% |
| Chemistry Increased alkaline phosphatase | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 35.0% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4 1.3% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 21.7% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4 0% |
| Chemistry Increased magnesium | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 26.9% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4 1.9% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 15.5% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4 0% |
| Chemistry Increased potassium | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 25.8% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4 2.6% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 15.5% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4 1.0% |
| Chemistry Decreased albumin | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 24.8% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4 0% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 5.2% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4 0% |
| Chemistry Increased creatinine | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 22.9% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4 0% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 20.6% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4 0% |
| Chemistry Increased sodium | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 21.8% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4 0% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 13.4% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4 0% |
| Laboratory Abnormality | ||||
| Hematology Decreased WBC | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 56.5% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4 1.3% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 61.9% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4 9.3% |
| Hematology Decreased neutrophils | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 53.3% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4 2.0% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 57.7% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4 11.3% |
| Hematology Decreased lymphocyte | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 52.6% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4 8.4% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 62.9% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4 15.5% |
| Hematology Decreased platelets | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 52.6% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4 3.3% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 39.2% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4 5.2% |
| Hematology Decreased hemoglobin | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 21.4% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4 0% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 90.7% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4 5.2% |
| Hematology Increased hemoglobin | Retevmo (n=158) Any Grade 20.1% | Retevmo (n=158) Grade 3/4 0% | Control Arm (n=98) Any Grade 1.0% | Control Arm (n=98) Grade 3/4 0% |
- Based on an interim analysis with a data cutoff date of May 1, 2023.7,10
- 10.1% (n=16) of patients permanently discontinued Retevmo (N=158) due to adverse events. 7.1% (n=11) were considered treatment-related, as assessed by trial investigator. Adverse events resulting in permanent discontinuation in ≥ 2 patients included increased ALT (n=2) and myocardial infarction (n=2)
- Serious adverse events occurred in 34.8% of patients who received Retevmo. The most frequently reported serious adverse events (in ≥2% of patients) were pleural effusion, hepatic function abnormal, ascites, cholecystitis, and pneumonia.
- More deaths were observed among those receiving Retevmo versus the entire control arm while on treatment or within 30 days of the last dose (n=7/158 vs n=0/98).
- More deaths were observed among those receiving Retevmo versus the entire control arm while on treatment or within 30 days of the last dose (n=7/158 vs n=0/98). Fatal adverse events occurred in 4.4% of patients; fatal adverse events included myocardial infarction (n=2), acute respiratory failure (n=1), cardiac arrest (n=1), malnutrition (n=1), respiratory failure (n=1), and sudden death (n=1). The deaths in 2 of 7 patients were judged by the investigators to be related to Retevmo (malnutrition and sudden death). One additional patient randomized to the control arm had a fatal event (respiratory failure) during crossover treatment with Retevmo.
- Dose interruptions and dose reductions due to adverse events occurred in 75.9% and 51.3% of patients who received Retevmo, respectively. See full Prescribing Information for dose modifications.
- Adverse events requiring dosage interruption in ≥5% of patients included increased ALT, increased AST, COVID-19, diarrhea, QT prolongation, and hypertension.
- Adverse events requiring dosage reductions in ≥2% of patients included increased ALT, increased AST, QT prolongation, hypertension, hepatic function abnormal, and platelet count decreased.
- Clinically relevant toxicities included decreased appetite (17.1%), hemorrhage (16.5%), interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis (4.4%), hypothyroidism (3.2%), hypersensitivity (2.5%), chylothorax (< 1%)
- Five randomized patients never received study drug and were excluded from the safety analysis.
- Graded according to National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI CTCAE) version 5.0.
AE=adverse event; ALT=alanine transaminase; AST=aspartate transferase; CTCAE=Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events; NCI=National Cancer Institute; RET=rearranged during transfection; WBC=white blood cell
Summary
In the 1L treatment of advanced or metastatic RET-fusion positive NSCLC
Retevmo is the first and only targeted agent to have demonstrated superior PFS in a Phase III head-to-head trial against pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy7,9
- LIBRETTO-431 (N=261) is a randomized, global, multicenter, open-label, Phase III trial that evaluated Retevmo versus chemotherapy with or without pembrolizumab in treatment-naive adult patients with advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive NSCLC, including those with brain metastases.
- The primary endpoint was PFS for Retevmo against chemotherapy with pembrolizumab and against the entire control arm.
- 10% of patients permanently discontinued treatment due to AEs with Retevmo (n=16/158)10
Retevmo may affect both healthy cells and tumor cells, which can result in side effects, some of which can be serious.1
Based on an interim analysis with a data cutoff date of May 1, 2023.7,9
Efficacy outcomes for patients treated with Retevmo (n=159) versus the entire control arm (n=102):
- Median PFS = 24.8 months (95% CI: 17.3, NE) vs 11.2 months (95% CI: 8.8, 16.8)
- ORR = 84% (95% CI: 77, 89) vs 63% (95% CI: 53, 72)
- Median DoR = 24.2 months (95% CI: 17.9, NE) vs 12.0 months (95% CI: 9.7, 23.3)
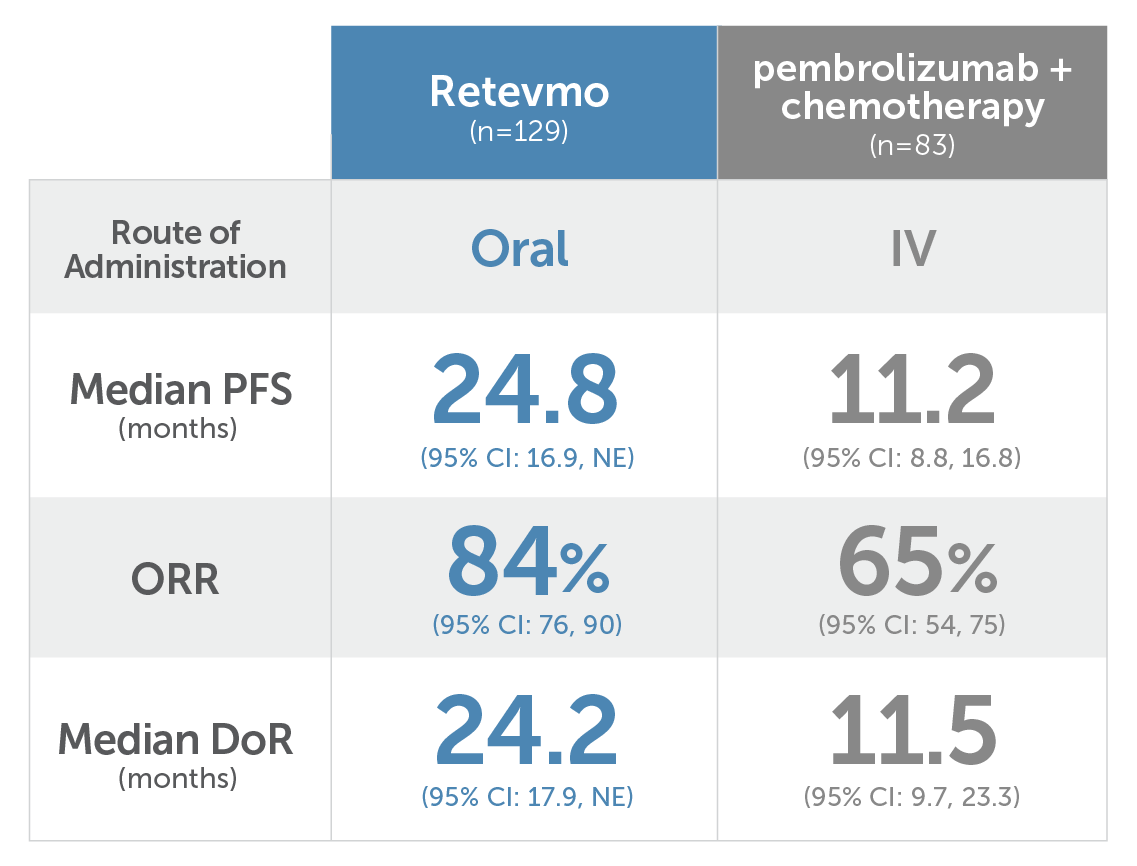
Median PFS for Retevmo (n=129) with oral administration was 24.8 months (95% CI: 16.9, NE). Median PFS for pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy (n=83) with IV administration was 11.2 months (95% CI: 8.8, 16.8). ORR for Retevmo was 84% (95% CI: 76, 90). ORR for pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy was 65% (95% CI: 54, 75). Median DoR for Retevmo was 24.2 months (95% CI: 17.9, NE). Median DoR for pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy was 11.5 months (95% CI: 9.7, 23.3).
1L=first line; CI=confidence interval; CNS=central nervous system; mDoR=median duration of response; INV=investigator; IRC=independent review committee; NE=not estimable; NSCLC=non-small cell lung cancer; ORR=objective response rate; RANO-BM=Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology Brain Metastases; RECIST=Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumours; RET=rearranged during transfection
NSCLC Summary
For patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC
Retevmo was granted approval based on LIBRETTO-001, a Phase I/II trial
LIBRETTO-001 Trial Design
The phase I/II, multicohort, open-label, single-arm, multicenter LIBRETTO-001 trial enrolled a pooled safety population of 796 patients, including 356 patients with locally advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive NSCLC.* Major efficacy outcomes were ORR and DoR, and were evaluated in 316 patients. Other efficacy outcomes, evaluated in subsets of patients, included CNS ORR, CNS DoR, PFS, OS, time to response, and best change in tumor size from baseline. In phase II, the dose for Retevmo was 160 mg PO BID.1-4
The pooled safety population also included 54 patients with advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive thyroid cancer (non-MTC),† 319 patients with advanced or metastatic RET-mutant MTC, 43 patients with RET fusion-positive solid tumors (other than NSCLC or thyroid),‡ and 24 patients with other cancers, including cancers without a RET alteration.3
*Patients with locally advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive NSCLC who had progressed on platinum-based chemotherapy and those without prior systemic therapy were enrolled in separate cohorts.1
†Non-MTC by histology included papillary (n=21), poorly differentiated (n=3), anaplastic (n=2), and Hurthle cell (n=1).1
‡Other RET fusion-positive solid tumors included pancreatic cancer (n=11), colon cancer (n=10), and salivary cancer (n=4)1.
BID=twice daily; CNS=central nervous system; DoR=duration of response; NSCLC=non-small cell lung cancer; ORR=objective response rate; OS=overall survival; PFS=progression-free survival; PO=orally; RET=rearranged during transfection.
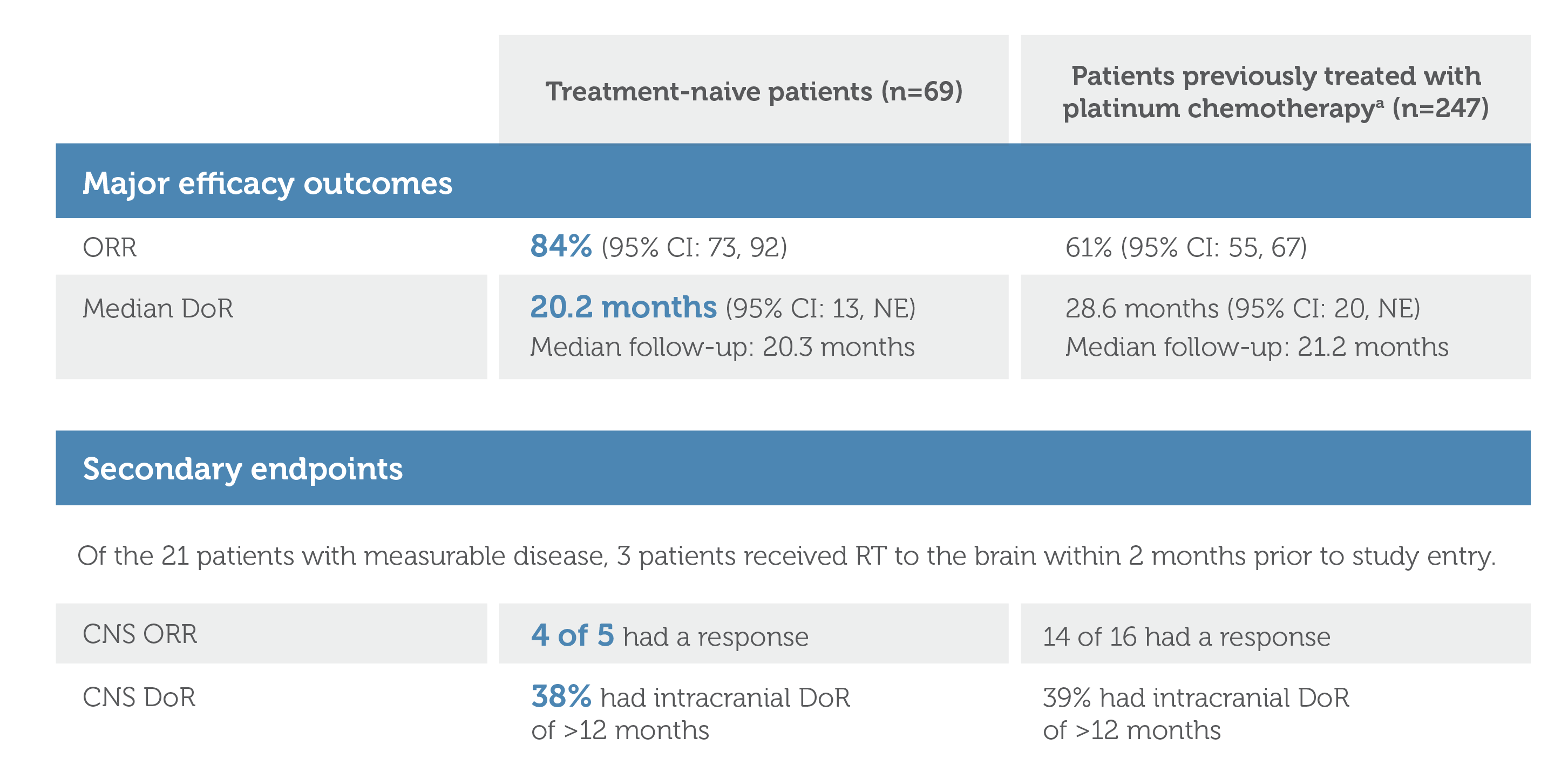
Graphic showing Major Efficacy Outcomes and Secondary Endpoints for treatment-naive patients (n=69) and patients previously treated with platinum chemotherapy (n=247; image footnote: Efficacy was evaluated in 247 adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive NSCLC who were previously treated with platinum chemotherapy enrolled into a cohort of LIBRETTO-001. All 247 patients received systemic therapy (with a median of 2 prior systemic regimens). Among treatment-naive patients (n=69), Objective Response Rate was 84% (95% confidence interval: 73, 92). Median Duration of Response (DoR) was 20.2 months (95% confidence interval: 13, NE). Median follow-up was 20.3 months. Among patients previously treated with platinum chemotherapy (n=247), Objective Response Rate was 61% (95% confidence interval: 55, 67). Median Duration of Response (DoR) was 28.6 months (95% confidence interval: 20, NE). Median follow-up was 21.2 months.
Secondary endpoints were CNS ORR and CNS DoR. Of the 21 patients with measurable disease, 3 patients received radiation therapy to the brain within 2 months prior to study entry. Among treatment-naive patients (n=69), 4 of 5 patients had CNS ORR response. On CNS DoR, 38% had intracranial DoR of greater than 12 months. Among patients previously treated with platinum chemotherapy (n=247), 14 of 16 had CNS ORR response. On CNS DoR, 39% had intracranial DoR of greater than 12 months.
- Time-to-event endpoints are not interpretable in a single-arm study. The clinical significance of this descriptive analysis is not known.
- ORR was defined as CR + PR and was assessed by IRC according to RECIST v1.1.1
- ORR, DoR, CNS ORR, CNS DoR results reviewed by an IRC.1,5
- CNS ORR was a prespecified secondary endpoint that was evaluated and confirmed by an IRC.1
* Efficacy was evaluated in 247 adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive NSCLC who were previously treated with platinum chemotherapy enrolled into a cohort of LIBRETTO-001. All 247 patients received systemic therapy (with a median of 2 prior systemic regimens).1
CI=confidence interval; CNS=central nervous system; CR=complete response; DoR=duration of response; IRC=independent review committee; NE=not estimable; NSCLC=non-small cell lung cancer; ORR=objective response rate; OS=overall survival; PFS=progression free survival; PR=partial response; RECIST=Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors; RET=rearranged during transfection; RT=radiation therapy
Select Important Safety Information
Hypertension occurred in 41% of patients, including Grade 3 hypertension in 20% and Grade 4 in one (0.1%) patient. Overall, 6.3% had their dose interrupted and 1.3% had their dose reduced for hypertension. Treatment-emergent hypertension was most commonly managed with anti-hypertension medications. Do not initiate Retevmo in patients with uncontrolled hypertension. Optimize blood pressure prior to initiating Retevmo. Monitor blood pressure after 1 week, at least monthly thereafter, and as clinically indicated. Initiate or adjust anti-hypertensive therapy as appropriate. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue Retevmo based on the severity.
References: 1. Retevmo (selpercatinib). Prescribing Information. Lilly USA, LLC. 2. Phase 1/2 study of LOXO-292 in patients with advanced solid tumors, RET fusion-positive solid tumors, and medullary thyroid cancer (LIBRETTO-001). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03157128. Updated June 9, 2022. Accessed June 14, 2022. 3. Data on File, Lilly USA, LLC, DOF-SE-US-0063. 4. Drilon A, Subbiah V, Gautschi O, et al. Durability of efficacy and safety with selpercatinib in patients with RET fusion+ non-small-cell lung cancer: LIBRETTO-001. Poster presented at: European Lung Cancer Congress; March 30–April 2, 2022. Poster 27P. 5. Drilon A, Subbiah V, Gautschi O, et al. Selpercatinib in patients with RET fusion-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: updated safety and efficacy from the registrational LIBRETTO-001 phase I/II trial. J Clin Oncol. 2023;41(2):385-394. 6. Solomon BJ, Zhou CC, Drilon A, et al. Phase III study of selpercatinib versus chemotherapy ± pembrolizumab in untreated RET positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Future Oncol. 2021;17(7):763-773. 7. Zhou C, Solomon B, Loong HH, et al. First-line selpercatinib or chemotherapy and pembrolizumab in RET fusion-positive NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(20):1839-1850. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2309457. 8. Data on File. Lilly USA, LLC. DOF-SE-US-0076. 9. Data on File. Lilly USA, LLC. DOF-SE-US-0077. 10. Data on File. Lilly USA, LLC. DOF-SE-US-0078.
INDICATIONS
Retevmo is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of:
- adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with a rearranged during transfection (RET) gene fusion, as detected by an FDA-approved test
- adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older with advanced or metastatic medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) with a RET mutation, as detected by an FDA-approved test, who require systemic therapy*
- adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older with advanced or metastatic thyroid cancer with a RET gene fusion, as detected by an FDA-approved test, who require systemic therapy and who are radioactive iodine-refractory (if radioactive iodine is appropriate)*
- adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors with a RET gene fusion that have progressed on or following prior systemic treatment or who have no satisfactory alternative treatment options*
*These indications are approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DoR). Continued approval for these indications may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.