Discover Head-to-Head Data for Retevmo versus current First Line Standards of Care and LIBRETTO-001
Retevmo is the first and only RET inhibitor indicated for advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive cancer, regardless of solid tumor type.1

Retevmo: The first precision oncology treatment approved by the FDA for certain RET-driven solid tumors, regardless of type1,2

Selpercatinib (Retevmo) is a National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)-recommended treatment option for certain patients with RET-positive metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and RET-positive advanced or metastatic thyroid carcinoma3,4*
*See the NCCN Guidelines for NSCLC for detailed recommendations, including other preferred treatment options.
See NCCN Guidelines® recommendationsNCCN makes no warranties of any kind whatsoever regarding their content, use or application and disclaims any responsibility for their application or use in any way.
The clinical data for Retevmo were from LIBRETTO-001, a phase I/II, multicohort, open-label, single-arm clinical trial.1,5
Click here to explore clinical trial design.
All results reviewed by an independent review committee (IRC).1,6-9
Retevmo demonstrated a robust and durable response in certain RET-driven cancers1
In treatment-naive patients with locally advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive NSCLC (n=69)1:
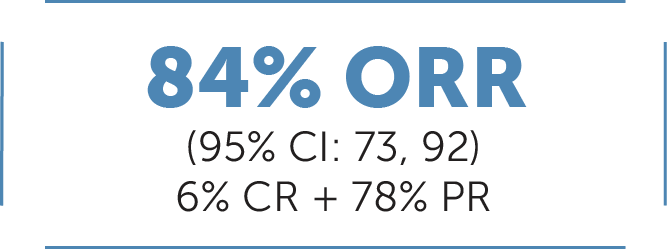
ORR was defined at CR+PR and was assessed by IRC according to RECIST v1.1.1
Median DoR 20.2 months (95% CI: 13, NE)1
Median follow-up: 20.3 months10
In patients previously treated† with platinum chemotherapy with locally advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive NSCLC (n-247)1:
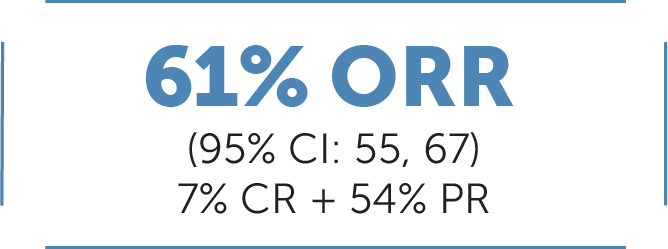
Median DoR 28.6 months (95% CI: 20, NE)1
Median follow-up: 21.2 months10
In systemic therapy-naive‡ patients with advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive thyroid cancer (non-medullary thyroid cancer (non-MTC))§ (n=8)1:

Median DoR not yet reached (95% CI: NE, NE)1
Median follow-up: 8.8 months9
In previously treatedǁ patients with advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive thyroid cancer (non-MTC) (n=19)1:

Median DoR 18.4 months (95% CI: 7.6, NE)1
Median follow-up: 17.5 months9
In cabozantinib/vandetanib treatment-naive patients with advanced or metastatic RET-mutant medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) (n=88)1:

Median DoR 22.0 months (95% CI: NE, NE)1
Median follow-up: 7.8 months9
In patients previously treated¶ with cabozantinib and/or vandetanib with advanced or metastatic RET-mutant MTC (n=55)1:

Median DoR not yet reached (95% CI: 19.1, NE)1
Median follow-up: 14.1 months9
ORR was defined as CR + PR and was assessed by IRC according to RECIST v1.1.1
In adult patients with other RET-driven solid tumor types (tumor agnostic, n=41)1#:
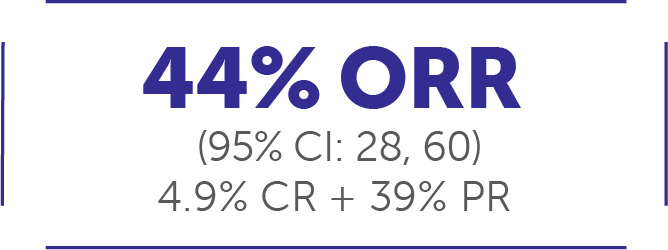
Median DoR 24.5 months (95% CI: 9.2, NE)1
Median follow-up: 14.9 months11
At the time of analysis (September 24, 2021), 50% of responses (n=9/18) were ongoing.11
The major efficacy outcome measures in LIBRETTO-001 were ORR and DoR.
All results reviewed by an IRC.1
Take action on RET. First, test. Then treat.
Select Important Safety Information
The labeling for Retevmo contains Warnings and Precautions for hepatotoxicity, interstitial lung disease (ILD)/pneumonitis, hypertension, QT interval prolongation, hemorrhagic events, hypersensitivity, tumor lysis syndrome (TLS), risk of impaired wound healing, hypothyroidism, and embryo-fetal toxicity. Monitor alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) prior to initiating Retevmo, every 2 weeks during the first 3 months of treatment, then monthly thereafter and as clinically indicated. Monitor for new or worsening pulmonary symptoms indicative of ILD/pneumonitis. Optimize blood pressure prior to initiating Retevmo. Monitor blood pressure after 1 week, at least monthly, and as clinically indicated. Monitor patients who are at significant risk of developing QTc prolongation, including patients with known long QT syndromes, clinically significant bradyarrhythmias, and severe or uncontrolled heart failure. Monitor the QT interval more frequently when Retevmo is concomitantly administered with strong and moderate CYP3A inhibitors or drugs known to prolong QTc interval. Permanently discontinue Retevmo in patients with severe or life-threatening hemorrhage. If hypersensitivity occurs, withhold Retevmo and begin corticosteroids at a dose of 1 mg/kg prednisone (or equivalent). See full Prescribing Information for further management instructions and dosage modifications for adverse reactions. Closely monitor patients that may be at risk of TLS (rapidly growing tumors, a high tumor burden, renal dysfunction, or dehydration) and consider appropriate prophylaxis including hydration. Withhold Retevmo for at least 7 days prior to elective surgery. Do not administer for at least 2 weeks following major surgery and until adequate wound healing. Monitor thyroid function before and periodically during treatment with Retevmo. Withhold until clinically stable or permanently discontinue Retevmo based on severity of hypothyroidism. Based on data from animal reproduction studies and its mechanism of action, Retevmo can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise females and males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Retevmo and for at least 1 week after the last dose. Serious adverse reactions occurred in 44% of patients who received Retevmo. The most frequent serious adverse reactions (in ≥2% of patients) were pneumonia, pleural effusion, abdominal pain, hemorrhage, hypersensitivity, dyspnea, and hyponatremia. Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 3% of patients; fatal adverse reactions included sepsis (n=6), respiratory failure (n=5), hemorrhage (n=4), pneumonia (n=3), pneumonitis (n=2), cardiac arrest (n=2), sudden death (n=1), and cardiac failure (n=1). Most common adverse reactions (≥25%) were edema, diarrhea, fatigue, dry mouth, hypertension, abdominal pain, constipation, rash, nausea, and headache. Most common Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (≥5%) were decreased lymphocytes, increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT), increased aspartate aminotransferase (AST), decreased sodium, and decreased calcium.
LIBRETTO-001 Trial Design
The phase I/II, multicohort, open-label, single-arm, multicenter LIBRETTO-001 trial evaluated Retevmo in patients with RET-altered advanced solid tumors. The pooled safety population included the following patients (n=796): advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive NSCLC** (n=356), advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive thyroid cancer (non-MTC)†† (n=54), advanced or metastatic RET-mutant MTC (n=319), and the tumor agnostic cohort of other locally advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive tumors, including pancreatic and CRC (n=43‡‡). Additionally, the overall safety analysis included 24 patients with other cancers, including cancers without a RET alteration. The study evaluated the following cohorts for efficacy: systemic therapy-naive patients (n=69) and previously treated patients who had progressed on platinum-based chemotherapy (n=247†) with advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive NSCLC; systemic therapy-naive (n=8‡††§§) and previously treated (n=19||††§§) patients with advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive thyroid cancer (non-MTC); patients with advanced or metastatic RET-mutant MTC that were cabozantinib and vandetanib-naive (n=88§§) and patients previously treated with cabozantinib and vandetanib (n=55¶§§), and patients in the tumor agnostic cohort (n=41||||). Major efficacy outcomes were ORR and DoR. Other efficacy outcomes included CNS ORR, CNS DoR, PFS, OS, time to response, and best change in tumor size from baseline. In phase II, the dose for Retevmo was 160 mg PO BID.1,5,10-12
†Efficacy was evaluated in 247 adult patients with advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive NSCLC who were previously treated with platinum chemotherapy enrolled into a cohort of LIBRETTO-001. All 247 patients received systemic therapy (with a median of 2 prior systemic regimens). 144 of the 247 patients received prior anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy, and 85 of the 247 patients received a prior MKI.10
‡Patients in this cohort received no prior systemic therapy other than radioactive iodine (RAI).1
§Primary tumor histologies included papillary thyroid cancer, poorly differentiated thyroid cancer, anaplastic thyroid cancer, and Hurthle cell thyroid cancer.1
‖Patients in this cohort received a prior systemic therapy (including sorafenib, lenvatinib, or both) other than RAI.1
¶The efficacy of Retevmo was evaluated in 55 patients with RET-mutant advanced MTC who were previously treated with cabozantinib or vandetanib enrolled into a cohort of LIBRETTO-001.1
#Efficacy was evaluated in 41 adult patients with advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive solid tumors. Thirty-seven patients received systemic therapy (with a median of 2 prior systemic regimens).1
**Patients with locally advanced or metastatic RET fusion-positive NSCLC who had progressed on platinum-based chemotherapy and those without prior systemic therapy were enrolled in separate cohorts.1
††Non-MTC by histology included papillary (n=21), poorly differentiated (n=3), anaplastic (n=2), and Hurthle cell (n=1).1
‡‡Efficacy was evaluated in 41 patients, including those with the following tumor types: pancreatic adenocarcinoma (n=11); colorectal (n=10); salivary (n=4); unknown primary (n=3); breast (n=2); sarcoma (soft tissue) (n=2); xanthogranuloma (n=2); carcinoid (bronchial) (n=1); carcinoma of the skin (n=1); cholangiocarcinoma (n=1); ovarian (n=1); pulmonary carcinosarcoma (n=1); rectal neuroendocrine (n=1); small intestine (n=1).1
§§Number of patients included in the initial efficacy analysis. Efficacy was based on patients who had at least 6 months of follow-up.12
||||Patients in this cohort received prior systemic therapies with a median of 2 prior systemic therapies (range 0-9).1
BID=twice daily; CI=confidence interval; CR=complete response; DoR=duration of response; NE=not estimable; NSCLC=non-small cell lung cancer; ORR=objective response rate; PO=orally; PR=partial response; RECIST=Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors; RET=rearranged during transfection.
See full trial resultsReferences: 1. Retevmo (selpercatinib). Prescribing Information. Lilly USA, LLC. 2. Drilon A, Hu ZI, Lai GGY, et al. Targeting RET-driven cancers: lessons from evolving preclinical and clinical landscapes. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018;15(3):151-167. 3. Referenced with permission from The NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer V5.2022. © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2022. All rights reserved. Accessed December 1, 2022. To view the most recent and complete version of the guidelines, go online to https://www.nccn.org. 4. Referenced with permission from The NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Thyroid Carcinoma V3.2022. © National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2022. All rights reserved. Accessed December 1, 2022. To view the most recent and complete version of the guidelines, go online to https://www.nccn.org. 5. Phase 1/2 study of LOXO-292 in patients with advanced solid tumors, RET fusion-positive solid tumors, and medullary thyroid cancer (LIBRETTO-001). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03157128. Updated June 9, 2022. Accessed June 14, 2022. 6. Data on File, Lilly USA, LLC, DOF-SE-US-0057. 7. Data on File, Lilly USA, LLC, DOF-SE-US-0058. 8. Data on File, Lilly USA, LLC, DOF-SE-US-0028. 9. Data on File, Lilly USA, LLC, DOF-SE-US-0032. 10. Drilon A, Subbiah V, Gautschi O, et al. Durability of efficacy and safety with selpercatinib in patients with RET fusion+ non-small-cell lung cancer: LIBRETTO-001. Poster presented at: European Lung Cancer Congress; March 30–April 2, 2022. Poster 27P. 11. Subbiah V, Wolf J, Konda B, et al. Tumor agnostic efficacy of selpercatinib in patients with RET fusion-positive solid tumors: a global, multicenter trial update (LIBRETTO-001). Presented at the ASCO Annual Meeting; June 3–7, 2022; Chicago, IL. 12. Data on File, Lilly USA, LLC, DOF-SE-US-0063.
INDICATIONS
Retevmo is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of:
- adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with a rearranged during transfection (RET) gene fusion, as detected by an FDA-approved test
- adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older with advanced or metastatic medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) with a RET mutation, as detected by an FDA-approved test, who require systemic therapy*
- adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older with advanced or metastatic thyroid cancer with a RET gene fusion, as detected by an FDA-approved test, who require systemic therapy and who are radioactive iodine-refractory (if radioactive iodine is appropriate)*
- adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors with a RET gene fusion that have progressed on or following prior systemic treatment or who have no satisfactory alternative treatment options*
*These indications are approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DoR). Continued approval for these indications may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in confirmatory trials.